
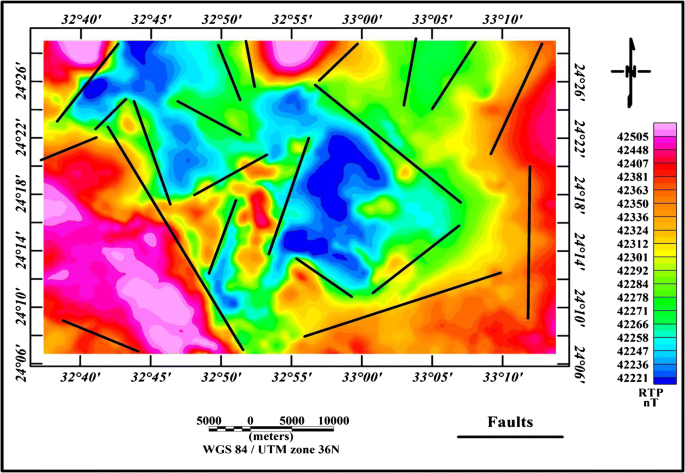
depth curve Line on a map or chart connecting points of equal depth below the datum.
Magnetic declination is the angular difference between ~ and true (geographic) north at the point of observation it is not constant but varies with time because of the "wandering" of the ~ pole. It is slowly moving in a north-westerly direction across the Arctic Ocean. It is presently located in Canadian Territorial waters, west of Greenland. It is the point that a magnetic compass points to. Let's take a look at a declination diagram that shows both Grid and ~ along with the bearing line to the cabin. We will likely need to make any adjustments to our north references as we move bearing between our our compass and our map. The corresponding bearings are called: true (or geodetic) bearing, grid bearing and magnetic (or compass) bearing. However, in practice three different directions are widely used: True North, Grid North and ~ (FAQ's nr. In principle, this reference line can be chosen freely. The Earth's magnetic field is believed to be generated by the planet's core. Magnetic Field The space influence by magnetic force. Magnetic Declination The horizontal angle be tween true north and ~ or true south and magnetic south. Instead, the compass shows magnetic bearing (also known as "compass" bearing). The direction from a point on the earth's surface following a great circle toward the ~ pole, indicated by the north-seeking end of a compass.īecause the ~ Pole is located hundreds of miles from the true North Pole the bearing shown by a compass will not the same as the true bearing. The location of the ~ pole changes slowly over time, but it is currently northwest of Hudson's Bay in northern Canada (approximately 700 km from the true north pole). ~ is determined by the earth's magnetic field and is not the same as true (or geographic) north. Compass needles point in this direction which differs from true geographic north. Magnetic North Pole: The magnetic north is a point in Northern Canada where the northern lines of attraction enter the Earth. The location where Earth's magnetic field dips vertically into the Earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
